Chess
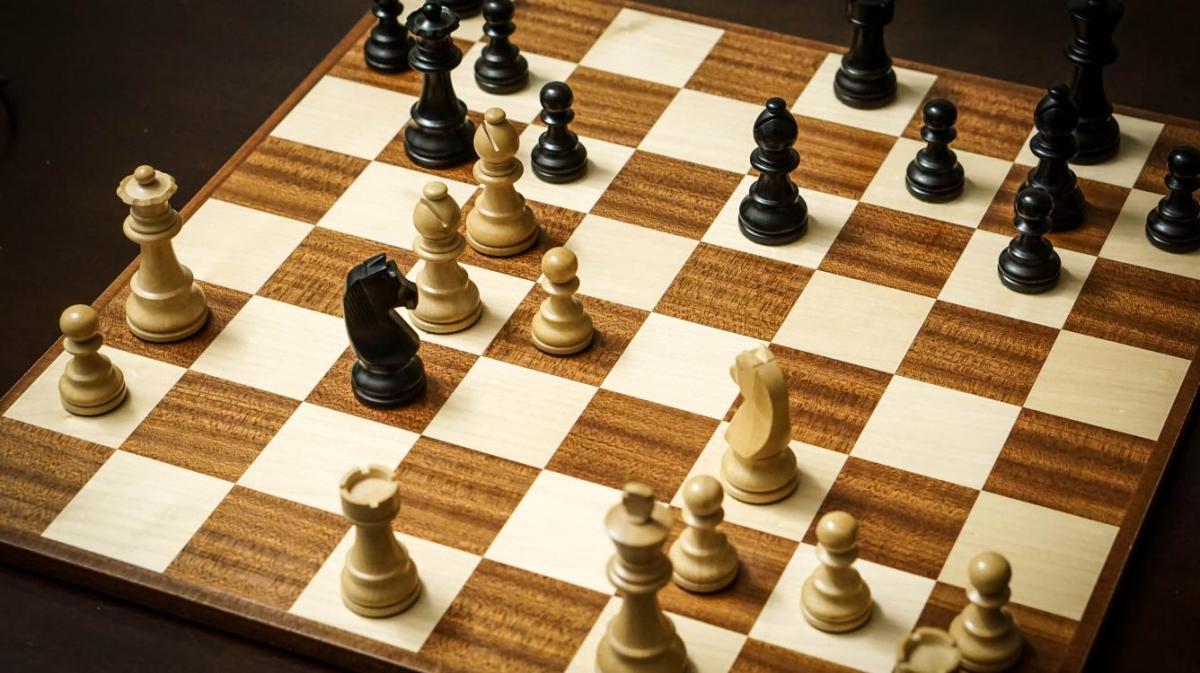

Chess, one of the oldest and most popular board games, played by two opponents on a checkered board with specially designed pieces of contrasting colours, commonly white and black. White moves first, after which the players alternate turns in accordance with fixed rules, each player attempting to force the opponent’s principal piece, the King, into checkmate—a position where it is unable to avoid capture. Chess first appeared in India about the 6th century AD and by the 10th century had spread from Asia to the Middle East and Europe. Since at least the 15th century, chess has been known as the “royal game” because of its popularity among the nobility. Rules and set design slowly evolved until both reached today’s standard in the early 19th century. Once an intellectual diversion favoured by the upper classes, chess went through an explosive growth in interest during the 20th century as professional and state-sponsored players competed for an officially recognized world championship title and increasingly lucrative tournament prizes. Organized chess tournaments, postal correspondence games, and Internet chess now attract men, women, and children around the world. This article provides an in-depth review of the history and the theory of the game by noted author and international grandmaster Andrew Soltis.